India grew to become the world’s most populous nation on Friday, ending China’s reign as No. 1, in keeping with an evaluation of United Nations inhabitants projections. The evaluation reveals that India’s inhabitants reached 1,425,782,975 on Friday.
India has overwhelming financial potential, not solely due of its inhabitants dimension, but additionally due to its demographic make-up. This monumental aggressive benefit may be seen in India’s dependency ratio.
The dependency ratio is a metric that compares a nation’s youth and aged, who don’t work, to its working inhabitants. The decrease the ratio, the less non-workers a rustic must help. So for instance, a nation with 50 dependents for each 100 employees can have a decrease dependency ratio than a nation with 90 dependents for each 100 employees.
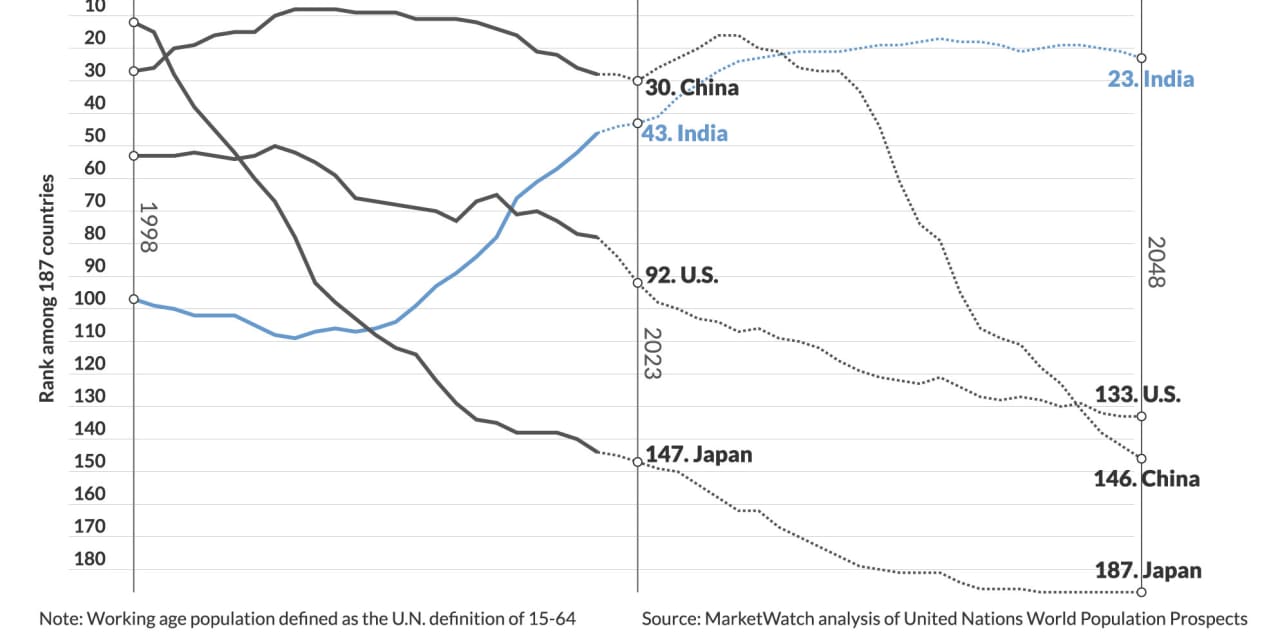
UN projections revealed in 2022 present that India’s dependency ratio is 47 dependents for each 100 employees in 2023, falling from the place it sat 25 years in the past at 68 dependents for each 100 employees. India’s dependency ratio is projected to fall to as little as 45-to-100 inside the subsequent 25 years earlier than it begins rising in 2033. However even then, India’s dependency ratio is projected to be ranked No. 23 on the earth in 2048, in comparison with its present rank of 43, primarily based on a MarketWatch evaluation of UN information. That’s an enormous edge for the world’s most populous nation.
As we speak, China’s dependency ratio is barely decrease than India’s at 45 dependents for each 100 employees. However China’s dependency ratio is ready to rocket larger within the years forward, as an growing portion of its inhabitants is made up of the younger and aged, supported by comparatively fewer working-aged adults. This case is essentially the results of China’s one-child coverage that led to 2016. China’s dependency ratio will begin rising in 2028 and attain 68-to-100 in 25 years, rating it 146th among the many world’s 193 international locations.
India’s benefit
The nation’s dependency ratio is projected to fall for the subsequent 15 years
Whereas demographic numbers point out India has a lot to achieve from its new standing because the world’s most populous nation, its full financial potential won’t be reached if it continues to lag behind different rising economies by way of labor productiveness and the feminine participation fee.
India is presently in its demographic dividend, a interval of financial development when the dependency ratio is low as a result of age construction of its inhabitants. A rustic is taken into account to be in its demographic dividend when its fertility fee falls, and extra girls and caretakers enter the workforce because of this, which usually interprets right into a decrease dependency ratio. However India may be leaving a few of its financial dividend on the desk.
A report from the United Nations Inhabitants Fund (UNPFA) outlines eight particular insurance policies and initiatives the nation ought to take to harness this pivotal interval in India’s historical past, centering round two pillars. The primary is particular person well being, which may be improved with extra funding of healthcare, reproductive well being and schooling. The second pillar is aimed toward shifting the construction of the financial system from agricultural to a producing base.
Nonetheless, the information factors from the U.N. report that measure the help in India for the primary pillar — the well being of a brand new working inhabitants — point out India is behind. Healthcare spending has not saved up with India’s rising gross home revenue, and unmet wants for household planning are excessive in comparison with close by international locations, like China and South Korea. Girls even have fewer alternatives to study expertise that will enhance their participation within the labor pressure, the report mentioned.
“With out correct insurance policies, the rise within the working-age inhabitants could result in rising unemployment, fueling financial and social dangers,” in keeping with the report.
India’s demographic numbers point out the nation has a lot to achieve from its rising workforce and certainly the nation has made some vital strides to help its financial transition. However India trails behind different rising and developed economies primarily based on some metrics, a new ebook from the World Financial institution reveals.
The World Financial institution’s measure of potential financial development is split into three classes— complete issue productiveness, capital accumulation and labor. Whereas the South Asia Area, of which India is grouped, is the one rising market and growing financial system (EMDE) to not have suffered a decline in total potential development prior to now decade in comparison with the ten years earlier than it, that’s primarily due to enhancements in complete issue productiveness and capital accumulation. Progress from capital accumulation and labor is the place India trails behind.
Whole issue productiveness, which happens through a extra environment friendly use of inputs via technological adjustments, has been the biggest contributor to potential financial development in South Asia prior to now 20 years, in keeping with the World Financial institution report. In India, complete issue productiveness far exceeds that of the three largest economies, the U.S., China and Japan. This may be attributed to India’s transition from an agricultural financial system to manufacturing.
Capital accumulation development potential in India is beneath China however above the U.S. and Japan, regardless that different international locations within the South Asia area — Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal — have sturdy funding. India’s weak capital accumulation potential is because of coverage uncertainties and structural bottlenecks from unreliable energy and transportation networks, in keeping with the World Financial institution report.
Labor is the world with the smallest quantity of financial development potential in India, in comparison with the 2 different classes. That is largely due to academic challenges that restrict the potential of labor to contribute extra to financial development in India, the place solely 40% of the inhabitants accomplished secondary college within the 2010s. That is solely a 5 share level enhance from the last decade prior, the second smallest of the six EMDE areas. And the pandemic’s influence on college completion charges can be a brand new wrench on this space of development potential, in keeping with the World Financial institution report.
“Human capital can have been eroded by decrease participation charges, disruptions to schooling, and a deterioration in well being outcomes.” in keeping with the World Financial institution’s report.
Whereas India has formidable reforms deliberate, the World Financial institution sees alternatives to speed up their implementation. The actions that can make the largest influence are people who formalize the workforce and encourage a better feminine labor participation fee to match that of different EMDEs.